Abstract
Background and Aim:
It is well known that hydroxyurea impacts on clinical and hematologic indices in sickle cell disease (SCD), we aimed to evaluate the effect of hydoxyurea on clinical and hematological improvement of Omani sickle cell disease pateints.
Methods and Materials
In this retrospective single-center study, we selected 18 Omani sickle cell disease patients aged above 18 years, who were started on Hydroxyurea 5-10mg/kg/day as per their standard of care and in whom the inclusion criteria fulfilled.
Inclusion criteria were history of more than three admissions with vaso-occlusive crises /year, history of acute chest syndrome, history of priapism, history of splenic sequestration crises.
Patients were excluded if they had follow-up of Less than six months, blood transfusion during the study, pregnant ladies.
In our study, we looked at the SCD patients who were followed in Haematology clinic in AFH every three months. As per the routine follow up of these patients in this hospital, patients were assessed in each visit for the number of crises, HPEL, CBC, LFT, UEG, and any reported side effects.
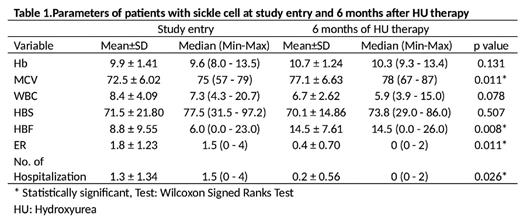
Our aim was specifically to observe the number of ER crises, number of hospital admissions, HBF, HB, MCV, WBC over six months post HU treatment .
The data collected based on the doctors notes & lab results from the Hospital information system. Side effects of the drug if any were observed from the prescription history.
The study was approved by the ethical committee in Armed Force Hospital in Muscat, Oman.
Data has been stored and analyzed in the SPSS program.
Results
In this study, we looked at 18 patients with SCD who were treated with HU 5-10mg/kg/day .
These patients consisted of 6 females and 12 males.
We found that in patients with sickle cell disease Hu significantly increased the HBF (P=0.008) and MCV (p=0.011) after six months.
There was no statistically significant difference between the baseline and after six months in HB (p=0 .131) and WBC ( P=0.078 ).
There was statistically decrease in the number of ER between baseline and six months ( p = 0.011) .
There was statistically significant decrease in the number of Hospitalizations between the baseline and the six months (p= 0.026).
Our study showed HU therapy was well tolerated by our patients and remarkable adverse effects were not reported in patients after six months treatment with HU.
Conclusion:
The results showed that the use of hydroxyurea 5-10 mg/kg/day for 6 months duration on patients with SCD significantly improve the HBF and MCV and decreased the number of ER crises and hospital admissions without any remarkable adverse effects.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal